Understand Marketing Environment | Macro, Micro & Internal Environment

Difference Between Microenvironment, Macroenvironment and Internal Environment
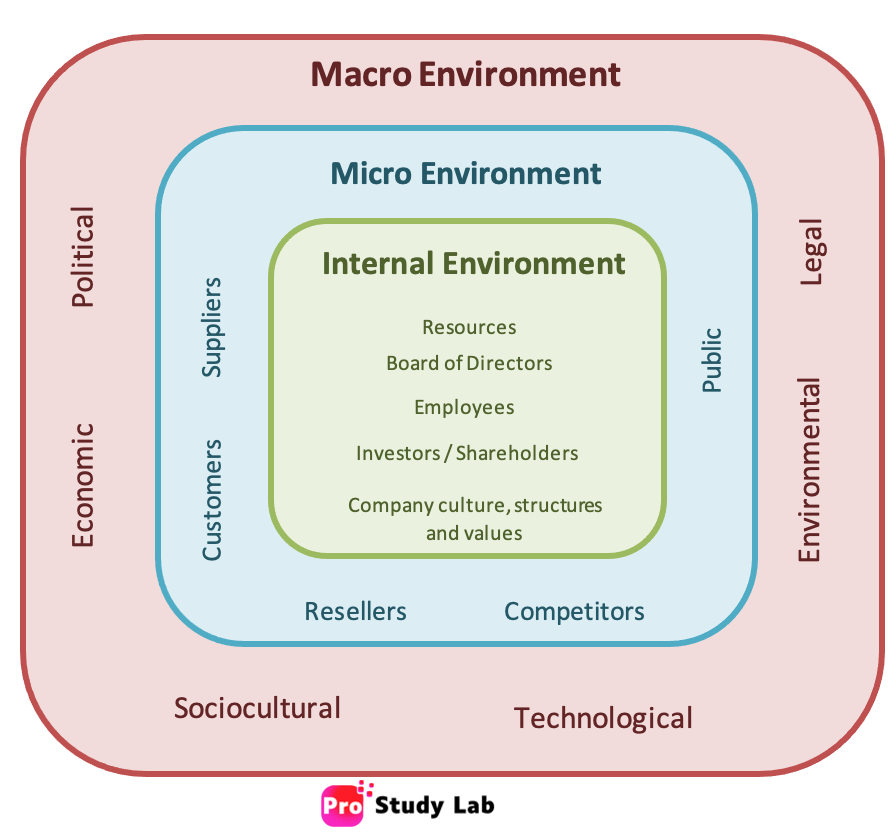
Any business operates in an environment that has different factors. This environment is also identified as the marketing environment. The marketing environment is a crucial concept in marketing that refers to the external and internal factors that can influence a company’s marketing efforts. It includes various elements, such as the macro environment, microenvironment (task environment), and internal environment. Thus, the marketing environment includes these internal and external factors that impact the company’s marketing decisions, both directly and indirectly. Therefore, a company’s internal factors are under its control, but external factors are beyond its control.
Let’s explore each of these components in more detail:
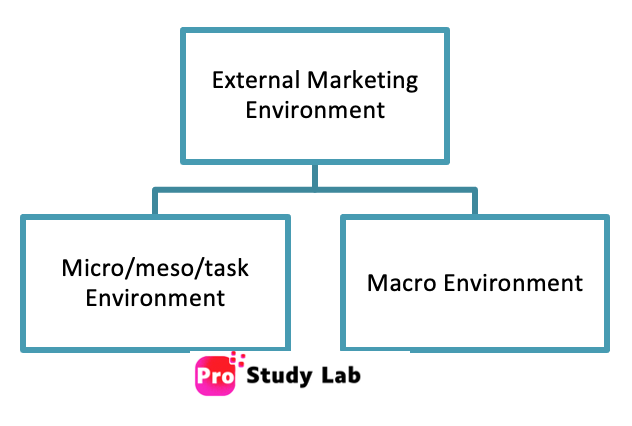
External Marketing Environment
All factors outside of an organization’s control are included in the external marketing environment. There are two elements identified within the external marketing environment: microenvironment and macroenvironment. These external variables are outside the marketers’ or company’s control, yet they still impact the decisions taken while developing a strategic marketing plan.
Macro Environment
The major social factors that impact a company’s decision-making and performance include the macro environment. These factors are uncontrollable for organisations. Generally, six major factors are identified under macro-environmental factors (PESTEL factors), but they can also expand into different sub-elements.
- Political
- Economic
- Social and cultural
- Technological
- Natural environmental
- Legal
- Demographic Factors: Characteristics of the population, such as age, gender, income, education, and cultural diversity, which can influence consumer behaviour and market segmentation.
- Economic Factors: Economic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, unemployment levels, and overall economic stability, that affect consumer purchasing power and business operations.
- Socio-Cultural Factors: Social and cultural influences, such as values, beliefs, attitudes, lifestyles, and trends, that shape consumer behaviour and demand for products or services.
- Technological Factors: Advances in technology, innovation, and digital transformation that impact product development, distribution channels, communication methods, and customer interactions.
- Political Factors: Government regulations, policies, and political stability that can affect business operations, trade barriers, taxation, and legal compliance.
- Environmental Factors: Concerns related to sustainability, climate change, natural resources, and environmental regulations that influence consumer preferences and corporate responsibility.
- Legal Factors: Laws, regulations, and legal frameworks that govern business activities, intellectual property rights, consumer protection, advertising standards, and competition laws.
Microenvironment / Task Environment / Meso Environment
Elements in a firm’s immediate environment that impact its performance and decision-making fall under micro-environment factors. The microenvironment consists of the actors and forces in a company’s immediate environment that directly influence its marketing activities. This also refers as the task environment as it covers assessing partnerships and collaborative relationships with other companies or organizations, such as joint ventures, strategic alliances, or supplier agreements, that support the company’s business goals.
Microenvironmental factors include:
- Suppliers
- Competitors
- Marketing intermediaries
- Consumers
- Publics
- Customers: The target market, including individuals or organizations that purchase or consume the company’s products or services. These are specific individuals or organizations with whom the company engages in business transactions, builds relationships, and focuses its marketing efforts.
- Suppliers: The individuals or organizations that provide the necessary inputs, such as raw materials, components, or services, for the company’s production or operations.
- Competitors: Other companies operating in the same industry or market that offer similar products or services, creating competitive rivalry.
- Intermediaries: Channels of distribution, such as retailers, wholesalers, or distributors, that facilitate the movement of products or services from the company to the end consumers.
- Publics: Groups or entities that have an interest in or can significantly influence the company’s operations, such as media, government agencies, financial institutions, and local communities.
- Marketing Intermediaries: Specific intermediaries, such as advertising agencies, public relations firms, or market research companies, that assist in the promotion and distribution of the company’s products or services.
Internal Environment
The internal environment refers to the factors within a company’s control that influence its marketing activities. It includes:
- Organizational resources
- Employees
- Shareholders
- Board of directors
- Investors
- Corporate culture
- Organizational structure
- Value system
- Company Culture: The values, beliefs, norms, and shared behaviours within the organization that shape its marketing strategies, decision-making processes, and customer interactions.
- Organizational Structure: The formal framework and hierarchy that determine how the company is organized and how marketing activities are planned, executed, and coordinated.
- Resources and Capabilities: The company’s tangible and intangible assets, including financial resources, human resources, technology, brand reputation, and core competencies, contribute to its marketing efforts.
- Marketing Strategy: The company’s overall approach to marketing, including its target
Hence, understanding the marketing environment is essential to develop effective marketing strategies.











